| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 용어
- error
- leetcode
- Github
- Reinforcement Learning
- Linux
- Python
- long video understanding
- quantification
- memory bank
- Artificial Intelligence
- 백준
- deeprl
- transference
- tensorflow
- MySQL
- Anaconda
- LeNet-5
- jmeter
- multimodal machine learning
- 코딩테스트
- sliding video q-former
- autogluon
- hackerrank
- CS285
- Kaggle
- CNN
- Server
- ma-lmm
- vision-language-action
- Today
- Total
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
- 용어
- error
- leetcode
- Github
- Reinforcement Learning
- Linux
- Python
- long video understanding
- quantification
- memory bank
- Artificial Intelligence
- 백준
- deeprl
- transference
- tensorflow
- MySQL
- Anaconda
- LeNet-5
- jmeter
- multimodal machine learning
- 코딩테스트
- sliding video q-former
- autogluon
- hackerrank
- CS285
- Kaggle
- CNN
- Server
- ma-lmm
- vision-language-action
- Today
- Total
Juni_DEV
[PaperReview] OpenVLA: An Open-Source Vision-Language-Action Model 본문
[PaperReview] OpenVLA: An Open-Source Vision-Language-Action Model
junni :p 2025. 6. 19. 12:54논문이 Appendix 빼고 11장, 합쳐서 37장 정도 되는데 Appendix에 실험 내용이 많다보니 내용이 좀 길다.

OpenVLA
- 7B parameter open-source VLA model
- trained on 970K robot episodes from the Open X-Embodiment dataset
- build on a Llama2 LM + visual encoder (pretrained features from DINOv2 + SigLIP)
- fully open-source and models can be downloaded and fine-tuned from HF
Background
There are two key reasons preventing the widespread use of existing VLAs:
- existing VLAs are largely closed and inaccessible to the public
- prior work fails to explore methods for efficiently fine-tuning VLAs for new tasks
- Robot manipulation을 위해 학습된 policy
→ Training data 이상으로 generalize 하기 어려움
→ vision and language are capable of these types of generalization and more.
Contribution
- strong results for GENERALIST MANIPULATION
- 29개 task와 multiple robot embodiments에서 RT-2-X(55B) 같은 closed model 보다 7x fewer parameters로 absolute task success rate(the percentage of users who completely and flawlessly complete a specific task)에서 16.5% 더 높은 성능을 보임.
- strong genralization result in multi-task environments involving multiple object
- strong language grounding abilities, and outperform expressive from-scratch imitation learning methods (such as Diffusion Policy) by 20.4%
- 7 diverse manipulation tasks spanning behaviors from object pick-and-place to cleaning a table.
- compute efficiency
- can be fine-tuned on consumer GPUs via modern low-rank adaptation methods and served efficiently via quantization without a hit to downstream success rate.
Related Works
Visually-Conditioned Language Models
fusing low-level spatial information from DINOv2 with higher-level semantics from SigLIP to aid in visual generalization.
Generalist Robot Policies
Generalist robot policies, like Octo, typically combine pretrained components with new modules, but OpenVLA's end-to-end approach fine-tunes VLMs to generate robot actions as language tokens, achieving superior performance and generalization.
Vision-Language-Action Models
Existing works on VLAs either focus on training and evaluating in single robot or simulated setups and thus lack generality, or are closed and do not support efficient fine-tuning to new robot setups
⇒ Our OpenVLA
(1) by combining a strong open VLM backbone with a richer robot pretraining dataset, OpenVLA outperforms RT-2-X in our experiments while being an order of magnitude smaller;
(2) we thoroughly investigate fine-tuning of OpenVLA models to new target setups, while RT-2-X does not investigate the fine-tuning setting;
(3) we are the first to demonstrate the effectiveness of ****modern PEFT and quantization approaches for VLAs;
(4) OpenVLA is the first generalist VLA that is open-source and thus supports future research on VLA training, data mixtures, objectives, and inference.
Method
Model Architecture

- a vision encoder that concatenates Dino V2 and SigLIP features while mapping image inputs to a number of “image patch embeddings”
- a projector that maps the output embeddings(= visual features) into the input space of a language model
- the LLM backbone, a Llama 2 7B-parameter large language model
VLMs Details
- During VLM training, the model is trained end-to-end with a next text token prediction objective on paired or interleaved vision and language data curated from various Internet sources.
- Prismatic-7B VLM
- 600M-parameter visual encoder, a small 2-layer MLP projector, and a 7B-parameter Llama 2 language model backbone
- two-part visual encoder ⇒ pretrained SigLIP + DinoV2 models.
- SigLIP, DinoV2, Llama 2는 학습 데이터 공개X, 인터넷 데이터로 구성되었을 가능성이 높음
- input image patch는 두 encoder를 각각 통과, 결과 feature vector는 channel 단위로 결합함.
- 단독 인코더보다 DinoV2를 추가하면 spatial reasoning 향상에 도움이 된다고 입증함.
- Prismatic-7B VLM
OpenVLA Training Procedure
fine-tune a pretrained Prismatic-7B VLM backbone for robot action prediction
“Vision-Language” task: observation image와 natural language task instruction를 예측된 로봇 액션 string으로 매핑하는 작업
- 연속적인 robot action을 language 모델의 tokenizer에서 사용하는 discrete token으로 매핑하여 LLM output space에 나타냅니다.
- robot actions의 각 차원을 256 bin 중 하나로 개별적으로 이산화합니다.
- 각 action 차원에 대해, 학습 데이터의 action 값에서 1th - 99th quantile 구간을 균등하게 나누어 구간 폭을 설정합니다.
- min-max bounds (RT-2) 대신 quantiles(분위수, 주어진 데이터를 동등한 크기로 분할)를 사용하는 이유는 데이터에서 outlier action을 무시하여 이산화 구간을 지나치게 확장하지 않고, 동작 이산화의 효과적인 세분성을 유지하기 위함.
- 이산화를 통해 우리는 N차원의 로봇 동작에 대해 [0... 255] 범위의 N개의 이산 정수를 얻습니다.
- 각 action 차원에 대해, 학습 데이터의 action 값에서 1th - 99th quantile 구간을 균등하게 나누어 구간 폭을 설정합니다.
- action 이 token sequence로 처리된 후, OpenVLA는 standard next-token prediction objective (이전 토큰들을 기반으로 다음에 올 토큰을 예측)로 학습되며, 예측된 action 토큰에 대해 cross-entropy loss을 평가합니다.
Training Data
The goal is to capture a large diversity of robot embodiments, scenes, and tasks.
Based on Open X-Embodiment (following OCTO with a few additions)
(1) a coherent input and output space across all training datasets
- 최소한 하나의 3인칭 카메라와 단일 로봇 팔 말단 조작기를 사용하는 manipulation dataset만 training dataset에 포함하도록 제한함
(2) a balanced mix of embodiments, tasks, and scenes in the final training mixture.
- 첫 번째 필터링을 통과한 모든 데이터셋에 대해 Octo의 데이터 혼합 가중치를 사용함
- Octo는 다양성이 적은 데이터셋을 경험적으로 가중치를 줄이거나 제거하고, 작업 및 장면 다양성이 큰 데이터셋의 가중치를 높이기 때문.
- DROID라는 데이터셋은 가중치 10%로 주고 했더니 action token 정확도가 낮게 유지(나중에 더 큰 혼합 가중치 또는 모델이 필요할 수 있다는 것을 뜻하는 건가?) → 품질 보장을 위해 final 3 of training에서는 제거했음
OpenVLA Design Decision
VLM과 다른 점이 많음
- Image Resolution: We compared VLAs with 224 × 224px and 384 × 384px inputs, but found no performance difference in our evaluations, while the latter takes 3x longer to train.
- Fine-Tuning Vision Encoder: we found fine-tuning the vision encoder during VLA training to be crucial for good VLA performance.
- Training Epochs: we found it important for VLA training to iterate through the training dataset significantly more times, with real robot performance continually increasing until training action token accuracy surpasses 95%(1 or 2 vs. 27).
Experiments
We aim to answer the following questions:
- How does OpenVLA compare to prior generalist robot policies, when evaluating on multiple robots and various types of generalization?
여러 로봇과 다양한 일반화 유형에 대해 평가할 때 OpenVLA는 이전의 일반 로봇 정책과 어떻게 비교되나요? - Can OpenVLA be effectively fine-tuned on a new robot setup and task, and how does it compare to state-of-the-art data-efficient imitation learning approaches?
새로운 로봇 설정과 작업에서 OpenVLA를 효과적으로 미세 조정할 수 있으며, 최첨단 데이터 효율적인 모방 학습 접근 방식과 비교하면 어떻게 다른가요? - Can we use parameter-efficient fine-tuning and quantization to reduce the computational requirements for training and inference of OpenVLA models and make them more accessible? What are the performance-compute trade-offs?
PEFT와 Quantization을 사용하여 OpenVLA 모델의 훈련 및 추론에 필요한 계산 요구 사항을 줄이고 접근성을 높일 수 있나요? 성능과 계산의 트레이드오프는 무엇인가요?
1. How does OpenVLA compare to prior generalist robot policies, when evaluating on multiple robots and various types of generalization?
- 각 환경에서 다양한 일반화에 걸쳐 포괄적인 평가 작업 세트를 정의
- 여러 객체가 있는 장면에서 사용자가 제공한 프롬프트에 따라 올바른 대상 객체를 조작할 수 있는지 확인하여 언어 조건 능력을 평가
- 이전 연구에서 수행한 평가보다 훨씬 더 높은 수준의 일반화를 테스트함.
(1) BridgeData V2 WindowsX
- 170 rollouts (17 tasks with 10 trials each)
- 4 types out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization tasks:
- visual/motion/physical/semantic generalization tasks + language grounding tasks



RT-1-X and Octo struggle on the tested tasks, often failing to manipulate the correct object
RT-2-X와 OpenVLA는 다른 모델들보다 훨씬 더 견고한 동작을 보였으며, 예를 들어 방해물이 있을 때 올바른 객체에 접근하고, 대상 객체의 방향에 맞추어 로봇의 엔드 이펙터를 적절히 정렬하며, 객체를 불안정하게 잡는 실수를 복구하기도 했습니다.
RT-2-X가 semantic generazation 작업에서 더 높은 성능을 달성했는데, 이는 더 대규모의 인터넷 사전 학습 데이터를 사용하고, 로봇 액션 데이터와 인터넷 사전 학습 데이터를 함께 co-finetuning 하여 사전 학습 지식을 더 잘 보존하기 때문으로 예상됩니다. 이는 로봇 데이터에만 파인튜닝된 OpenVLA와는 차별점입니다.
(2) Google Robot Evaluation
- 60 rollouts (12 tasks with 5 trials each)
- in-distribution tasks and out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization tasks


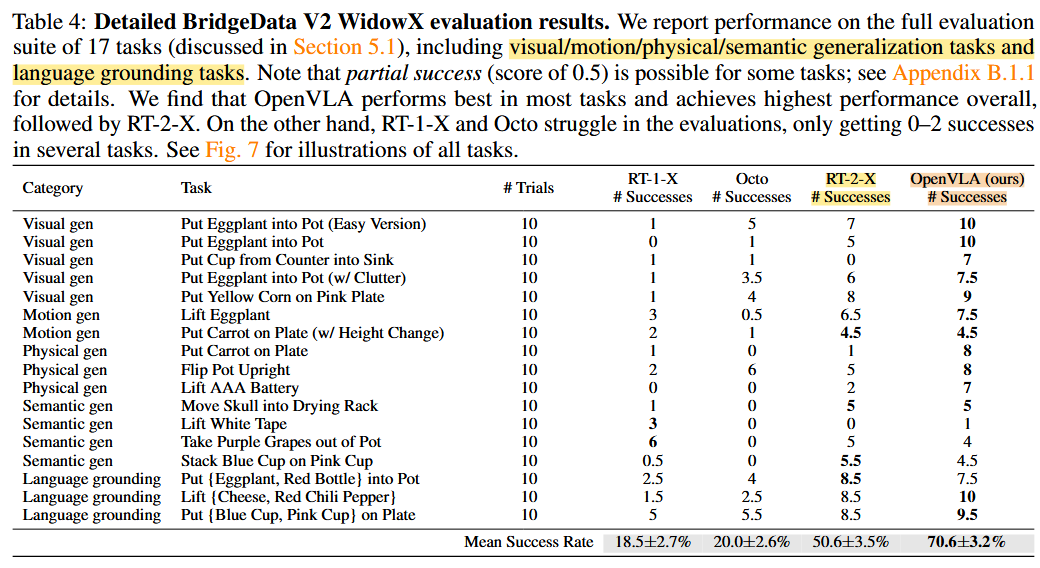
- RT-1-X and Octo experience difficulty on the evaluation tasks
- often unable to achieve a single success out of five trials in several tasks.
- RT-2-X and OpenVLA demonstrate strong performance, completing every task at least two times out of five trials
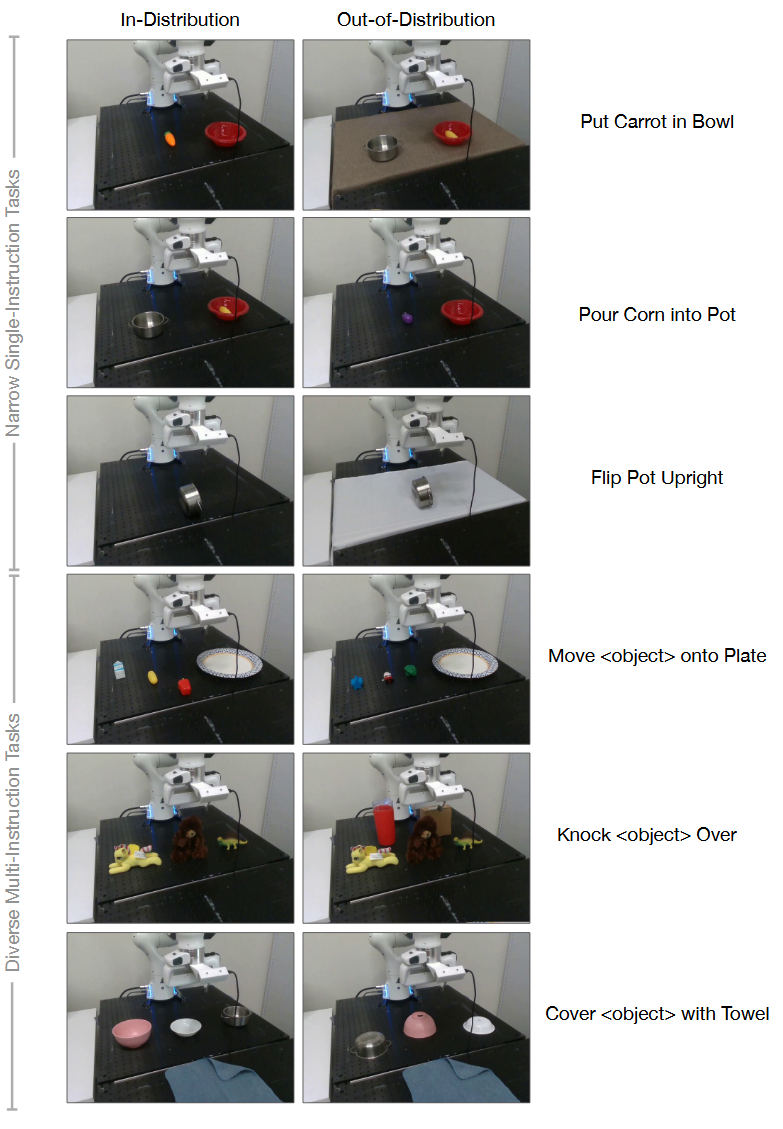
2. Can OpenVLA be effectively fine-tuned on a new robot setup and task, and how does it compare to state-of-the-art data-efficient imitation learning approaches?
OpenVLA가 실제 새로운 로봇 환경에 얼마나 빠르게 적응할 수 있는지를 조사


모델의 모든 파라미터를 완전히 파인튜닝하며, collect 10–150 demonstrations of each of 7 tasks. Each method with 10–12 in-distribution trials and 5–6 OOD generalization trials.
- Franka-Tabletop: 고정된 테이블에 장착된 Franka Emika Panda 7-DoF 로봇 팔.
- Franka-DROID: 최근 공개된 DROID 데이터셋의 Franka 로봇 팔 설정으로, 이동식 스탠딩 책상에 장착된 상태.

OpenVLA를 다음의 방법들과 비교합니다:
- Diffusion Policy: state-of-the-art data-efficient imitation learning approach, trained from scratch
- Diffusion Policy (matched): Diffusion Policy that matches the input and output specifications of OpenVLA.
- Octo: fine-tuned on the target dataset, since it is currently the best generalist policy that supports fine-tuning
- OpenVLA (scratch): OpenX로 사전 학습된 OpenVLA 모델이 아닌, 기본 Prismatic VLM을 직접 목표 로봇 설정에 맞춰 파인튜닝하여 대규모 로봇 사전 학습의 이점을 평가하는 실험입니다.
Diffusion Policy는 narrower single-instruction tasks에서 강력한 성능을 보이는 반면, Octo와 OpenVLA는 여러 지시문과 방해물 객체가 포함된 다양한 파인튜닝 작업에서 더 나은 성능을 보였습니다. → better adapt to these more diverse tasks where language grounding is important
OpenVLA는 모든 작업에서 최소 50% 이상의 성공률을 달성한 유일한 접근법으로, 특히 다양한 언어 지시문이 포함된 모방 학습 작업에서 강력한 기본 옵션이 될 수 있음을 시사합니다.
3. Can we use parameter-efficient fine-tuning and quantization to reduce the computational requirements for training and inference of OpenVLA models and make them more accessible? What are the performance-compute trade-offs?
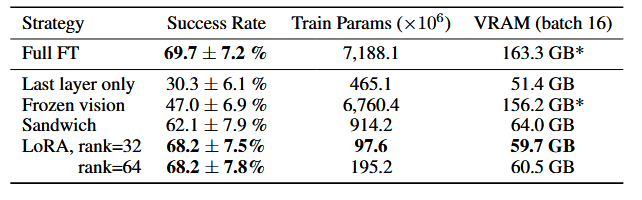
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
LoRA achieves the best trade-off between performance and training memory consumption.
Quantization
OpenVLA, a 7B-parameter model, consumes more memory at inference time than prior open-source generalist policies.

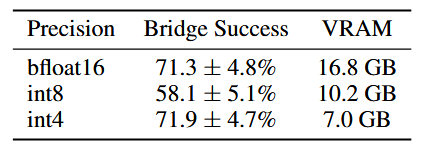
OpenVLA model with 8-bit and 4-bit precision on BridgeData V2 tasks.
- We observe that 8-bit quantization slows down inference across most GPUs, due to the overhead of the added quantization operations.
- 4-bit inference achieves higher throughput, since reduced GPU memory transfer compensates for the quantization overhead.
Appendix D. Ablation Study

- OpenX (reduction of 30% in absolute success rate)
- Language grounding은 괜찮았지만, 다른 generalization에는 큰 영향
- SigLip-Dinov2 vs. SigLip-only
- 5 percent reduction
- 일부 경우에만 generalization에 도움을 주는 것으로 보임
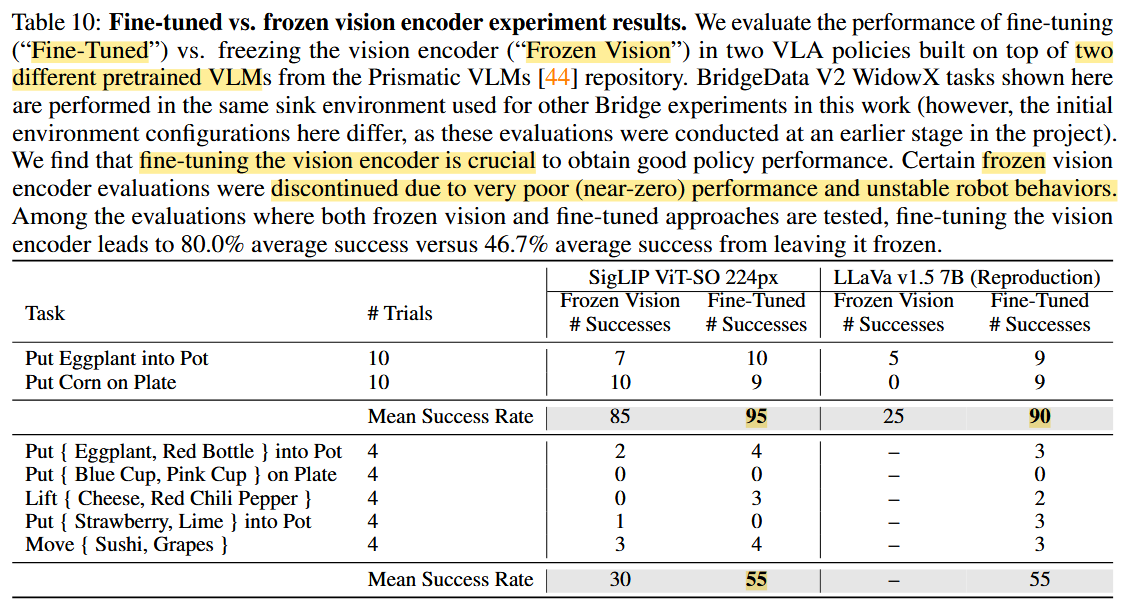
- fine-tuned vs. fixed vision-encoder
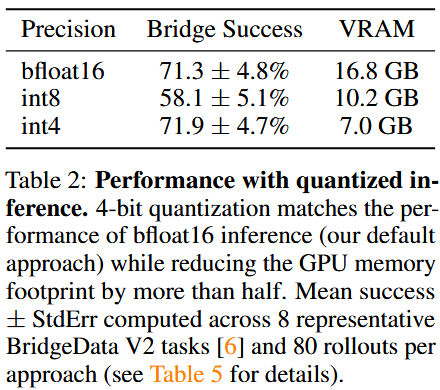
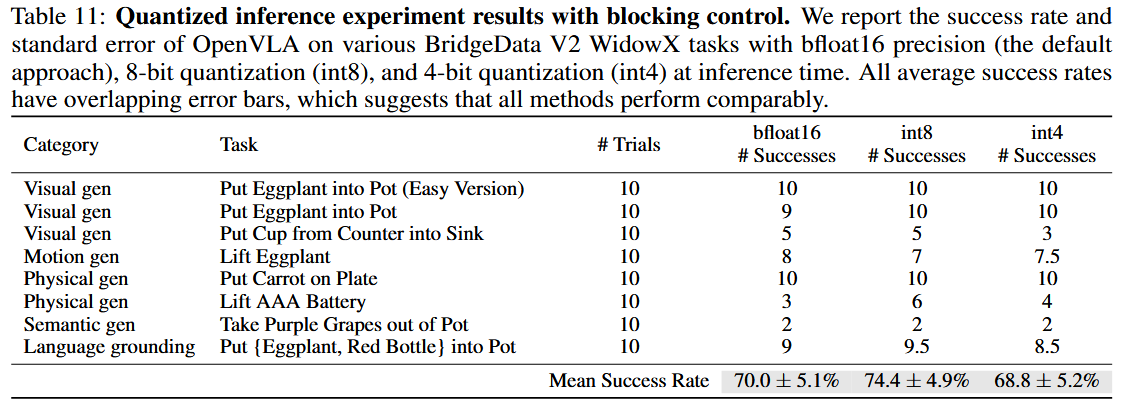
- policy performance ↔ model inference speed ⇒ quantized inference results
- 표 2에서는 8-bit 양자화가 낮은 추론 속도로 인해 가장 낮은 롤아웃 성능을 보였지만,
- 작업 성능에 대한 추론 속도의 영향을 제거하기 위해 차단 제어로 평가했을 때, 8-bit 양자화가 bfloat16 정밀도 및 4-bit 양자화와 유사한 성능을 보였습니다.
Discussion and Limitations
- only supports single-image observations.
- improving the inference throughput of OpenVLA is critical
- further performance improvements. → does not yet offer very high reliability on the tested tasks.
- many VLA design questions remain underexplored
- due to compute limitations, many VLA design questions remain underexplored
- What effect does the size of the base VLM have on VLA performance?
- Does co-training on robot action prediction data and Internet-scale vision-language data substantially improve VLA performance?
- What visual features are best-suited for VLA models?
Question & Answering
- Octo의 데이터 혼합 가중치를 사용함
- Octo는 다양성이 적은 데이터셋을 경험적으로 가중치를 줄이거나 제거하고, 작업 및 장면 다양성이 큰 데이터셋의 가중치를 높이기 때문.
- DROID라는 데이터셋은 가중치 10%로 주고 했더니 action token 정확도가 낮게 유지(suggesting a larger mixture weight or model may be required to fit its diversity in the future, 나중에 더 큰 혼합 가중치 또는 모델이 필요할 수 있다는 것을 뜻함?) → 품질 보장을 위해 final 3 of training에서는 제거했음
- fine-tuning vision encoder 같은 경우에는 VLA task 맞춤으로 fine-tuning 해야 성능이 향상된다는 점은 이해했음. → Appendix D.3에 ablation study 도 있네
- resolution 이랑 epoch은 왜?
- Appendix C에서 - original version of the BridgeData V2 dataset contained many transitions with all-zero (no-op) actions
- RT-2-X의 경우 simply second query를 선택하는 것과 동적으로 second query(first query가 zero인 경우)를 비교했는데 전자가 더 성능이 좋았다고 함
- 논문에서는 query pipeline의 latency 때문에 간섭이 있어 미묘한 성능 저하로 이어진다고 했는데 이해가 잘 안 됨
1번 step → action이 대부분 0이 나오는 거?
나올 수도 있고 안 나올 수도 있음
- 1번 step → 다 버리기
- 데이터 ⇒ 1번 step 자체가 말썽인 경우가 많음
- time series sensor
- 1번 step이 0인 것만 → 2번 쓰기 ⇒ 나름 거른 건데...
1이 더 성능이 좋음
OpenVLA: An Open-Source Vision-Language-Action Model
OpenVLA: An Open-Source Vision-Language-Action Model
openvla.github.io
https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.09246
OpenVLA: An Open-Source Vision-Language-Action Model
Large policies pretrained on a combination of Internet-scale vision-language data and diverse robot demonstrations have the potential to change how we teach robots new skills: rather than training new behaviors from scratch, we can fine-tune such vision-la
arxiv.org




